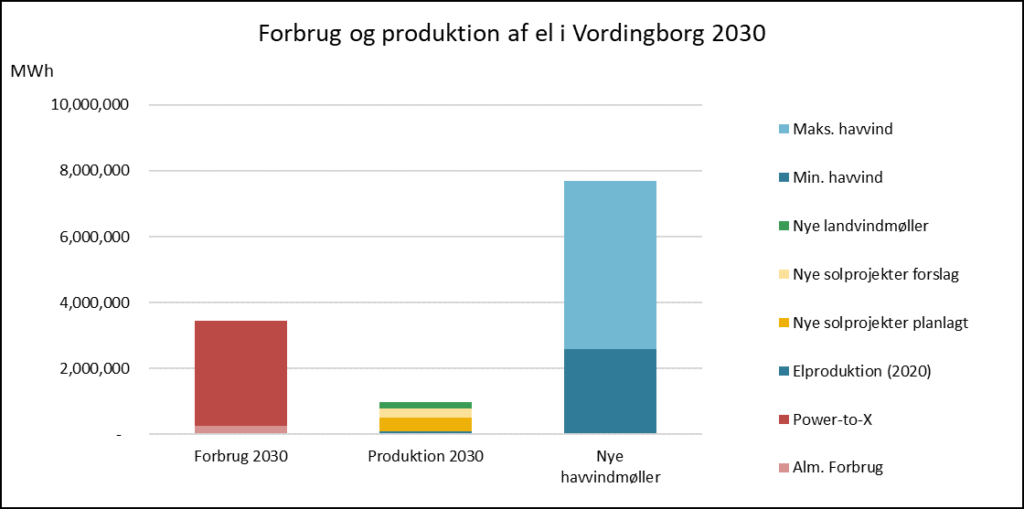
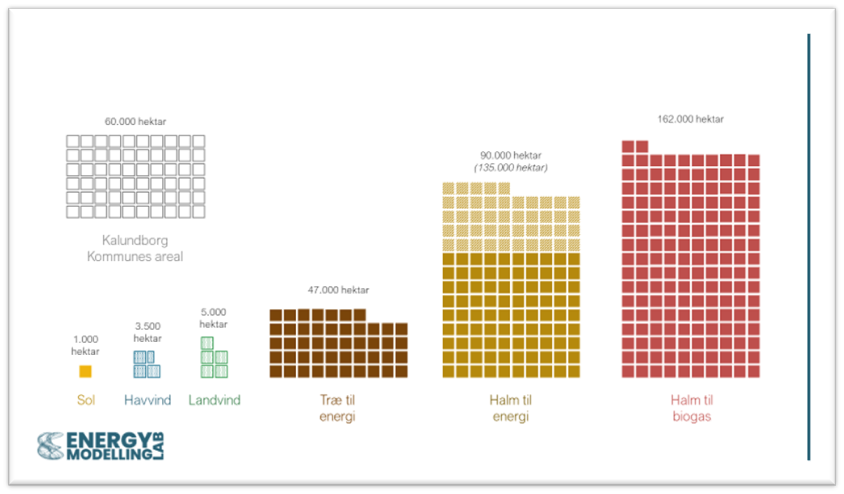
Energy Modelling Lab has contributed to the background study “The Value of Early Action on Energy Efficiency”. The study is focusing on buildings and industries. We identified key energy efficiency messages that we presented at the IEA Energy Efficiency Conference 2022 (see full presentation below). The conference took place in the Danish city of Sonderborg.
In collaboration with our partners, we examined the importance of early action on energy efficiency. We considered the costs of delayed progress. Furthermore, we looked into the benefits of achieving energy efficiency milestones on the way to reaching net zero emissions by 2050. The study was contracted by the International Energy Agency and financed by Danfoss.
Key findings on early action
![]() Early action matters. A low energy efficiency pathway would increase final energy consumption by 39%. CO2 emissions increase by 16% if action is delayed by 10 years.
Early action matters. A low energy efficiency pathway would increase final energy consumption by 39%. CO2 emissions increase by 16% if action is delayed by 10 years.
![]() Energy efficiency is the most effective measure to quickly improve energy security and lower electricity prices.
Energy efficiency is the most effective measure to quickly improve energy security and lower electricity prices.
![]() Reduced air pollution in a global net zero emissions scenario can reduce the cost of global health impacts by almost €500 bn in 2030.
Reduced air pollution in a global net zero emissions scenario can reduce the cost of global health impacts by almost €500 bn in 2030.
![]() Water heaters provide the biggest shifting potential and thereby CO2 emission reductions. Due to high savings and load-shifting potential, water heaters should be one of the first products to be digitized.
Water heaters provide the biggest shifting potential and thereby CO2 emission reductions. Due to high savings and load-shifting potential, water heaters should be one of the first products to be digitized.
![]() In process industries maintenance and simple upgrade of process plants can save 5 to 10% with very short payback time.
In process industries maintenance and simple upgrade of process plants can save 5 to 10% with very short payback time.
![]() The use of electromagnetic sources for process heat is in an early stage but holds promising potential for saving energy with a factor of 10 or more.
The use of electromagnetic sources for process heat is in an early stage but holds promising potential for saving energy with a factor of 10 or more.
We used the IEA’s Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario as a central focus and reference case for the analysis. Correspondingly, we focused on the implications and impacts of action within this decade, in all major energy-using regions globally.
Scenario analyses
We analyzed scenarios of low energy efficiency and high energy efficiency and estimated the accumulated final energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and air pollution.

Results
We presented the key findings at the International Energy Agency (IEA) Energy Efficiency Conference 2022 in the Danish city of Sønderborg.
Duration: January-April 2022
Client: International Energy Agency (IEA) and Danfoss
Budget: DKK 596,000
Partners: Energiforsk, Viegand Maagøe
Reference: Markus Wråke, CEO, Energiforsk
EML team: Kenneth Karlsson and Ida Græsted Jensen